In-Orbit Servicing & Manufacturing (ISAM)
Leading the development of mission autonomy for automated satellite rendezvous and servicing operations.

The Challenge
In-orbit servicing represents one of the most promising frontiers in space technology. The ability to refuel, repair, or upgrade satellites already in orbit could dramatically extend their operational lifetimes and reduce space debris. However, autonomous rendezvous and proximity operations present significant technical challenges.
A servicing satellite must detect, track, and approach a client satellite while managing its own resources and responding to unexpected situations. This requires sophisticated mission planning that integrates sensing, perception, dynamics, and control into a cohesive autonomous system.
My Contribution
I lead the R&D of the mission autonomy subsystem, responsible for high-level decision-making and mission planning. This involves:
- Mission design — Developing the operational concept and defining the autonomous behaviours required for different mission phases
- Requirements capture — Working with industry stakeholders to define system requirements and technical roadmaps
- Cross-team collaboration — Interfacing with guidance, sensing, perception, dynamics, and control teams to ensure cohesive system integration
The project has progressed through Mission Concept Review, System Requirements Review, Preliminary Design Review, and Critical Design Review, each delivered and presented to partners and stakeholders.
Technical Approach
The mission autonomy system provides a hierarchical planning architecture that manages the full servicing mission:
- Strategic planning — High-level mission sequencing and resource allocation
- Tactical planning — Trajectory optimisation for approach and proximity operations
- Reactive control — Real-time response to sensor feedback and anomalies
A key innovation is the integrated framework that connects mission design decisions with guidance algorithms, ensuring that high-level objectives translate into achievable trajectories while respecting all operational constraints.
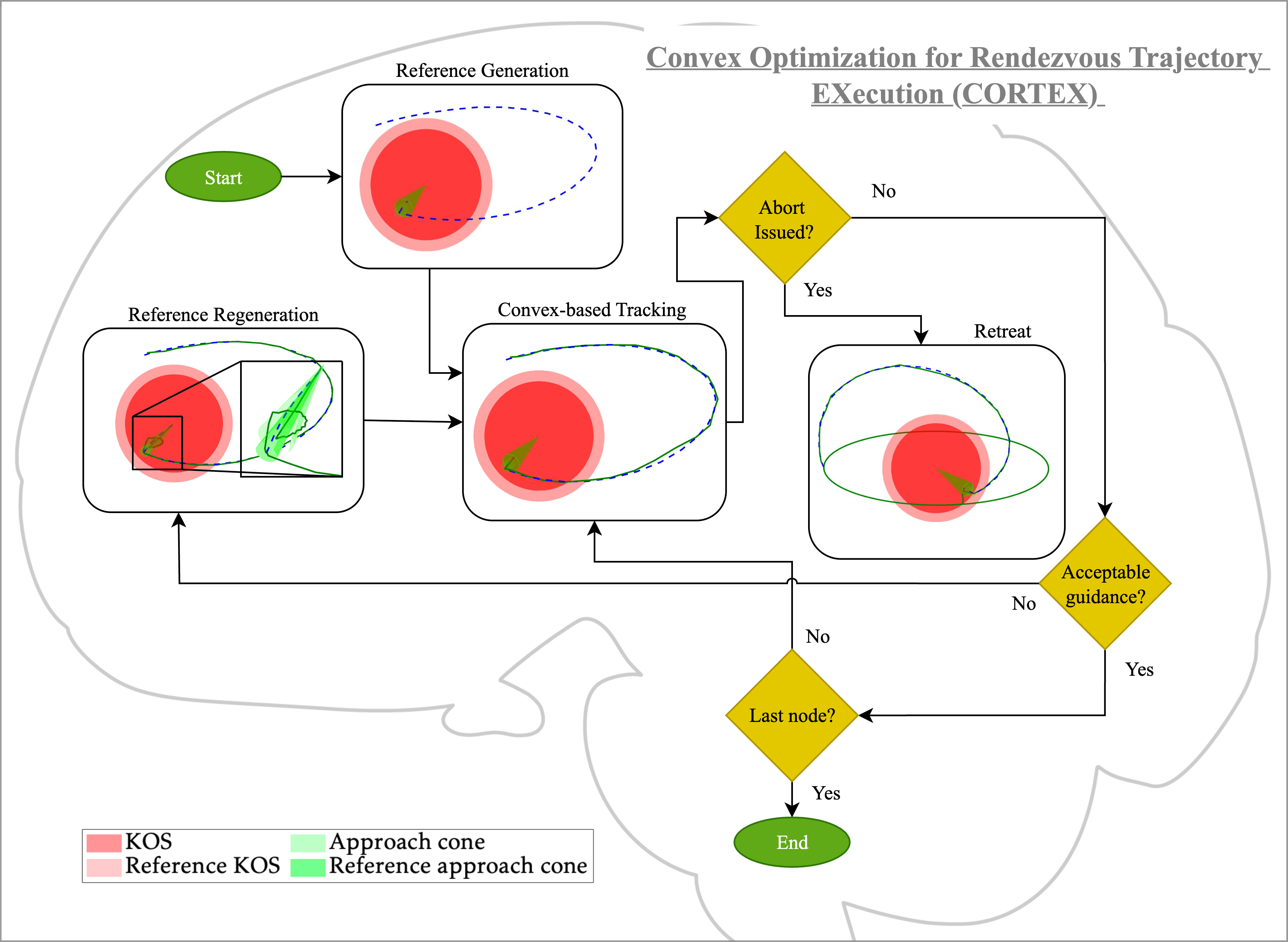
Results & Impact
The project has produced multiple publications at leading international conferences, including four papers at the 76th International Astronautical Congress (IAC 2025) covering mission design, trajectory optimisation, and system integration.
The hardware-in-the-loop testbed developed by the team enables realistic validation of autonomous rendezvous algorithms, representing a significant capability for Australian space research.
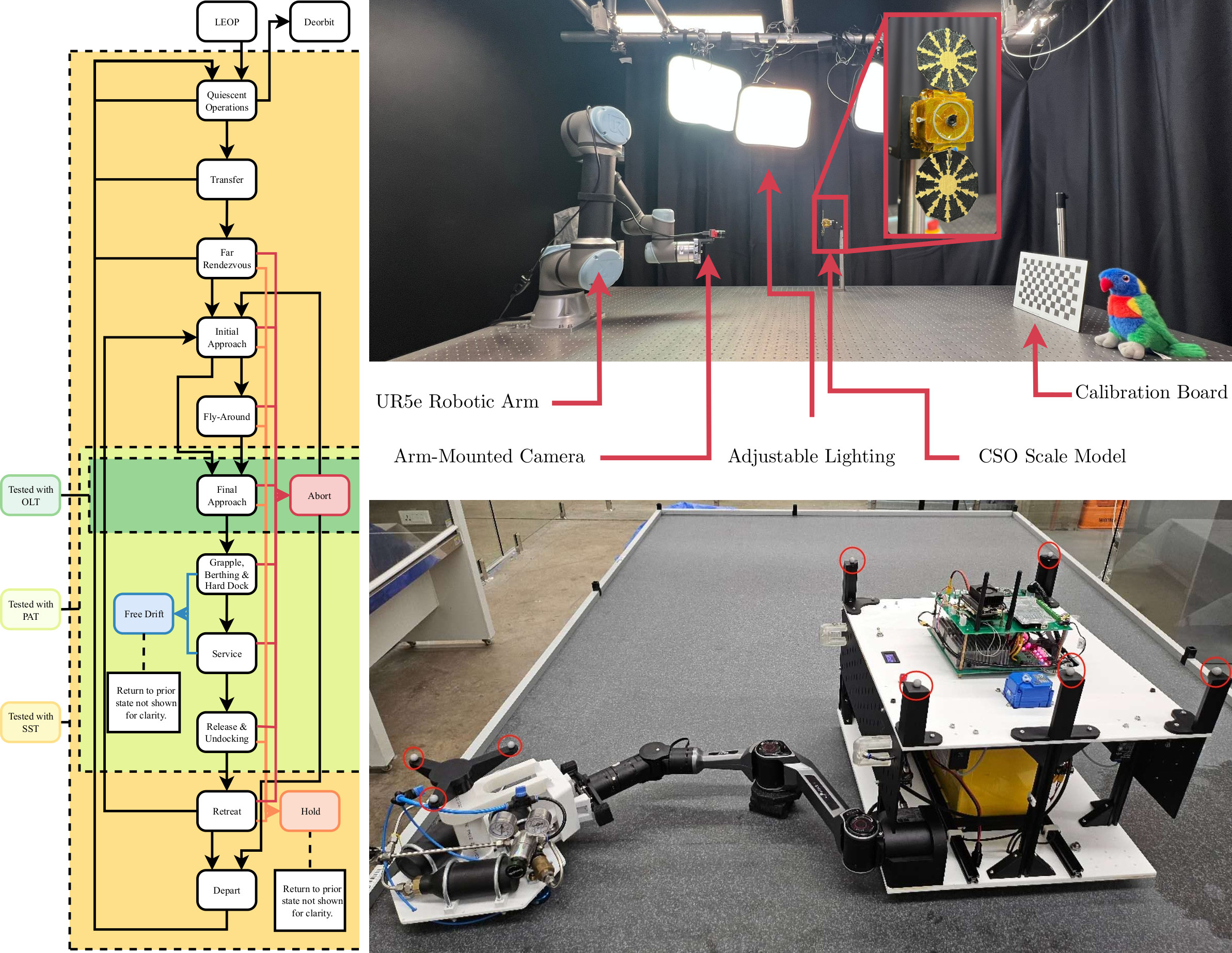
Broader Significance
ISAM capabilities are increasingly recognised as essential for sustainable space operations. By enabling satellite life extension and active debris removal, this technology addresses the growing challenge of orbital congestion while creating new commercial opportunities in the space sector.